0%
Ever tried running a project blind? Not knowing what's about to hit you? We've all been there. Most project managers are flying blind—hoping for the best while secretly preparing for the worst. But hope isn't a strategy.
Enter the risk register—your insurance policy against project disasters. It’s the place where every potential threat gets logged, assessed, and paired with a clear plan of action. Think of it as your survival guide through uncertainty. No fluff, no corporate jargon—just the facts.
Demand for these tools has skyrocketed because winging it doesn’t cut it anymore. The managers who thrive are the ones who track every threat, score its probability and impact, and assign ownership. They don’t guess—they calculate. They know which risks could derail a project and how to prioritize them.
Cybersecurity? That’s a whole different ballgame. Digital threats need their own specialized cyber risk register, packed with unique challenges and mitigation strategies.
Ready to stop gambling with your projects? Buckle up—we’re breaking down everything you need: real examples, practical implementation, and the best tools to get the job done.
Before we dive in, let’s define risk register: a risk register is more than a list—it’s the backbone of smart project management. At its core, a risk register systematically captures every potential risk that could throw a project off course. Each entry isn’t just a note; it includes a detailed description, the likelihood of occurrence, the potential impact, and an actionable mitigation plan.
Why a Risk Register Matters:
It’s not just for general project risks either. In cybersecurity, teams use specialized risk registers to track digital threats. Each cyber risk has unique characteristics, from vulnerabilities to regulatory implications, that need careful monitoring.
In short, a risk register transforms uncertainty into insight. It equips teams to prioritize threats, assign responsibility, and execute mitigation strategies effectively. For any project manager—or team handling sensitive systems—it’s the difference between chaos and control.
A risk register isn’t complicated. Skip the essentials, and it’s just paperwork. Do it right, and it becomes a powerful tool to track, assess, and manage risks—turning uncertainty into actionable insight. It guides decisions, keeps stakeholders aligned, and helps teams focus on what truly matters.
A good risk register has six core components:
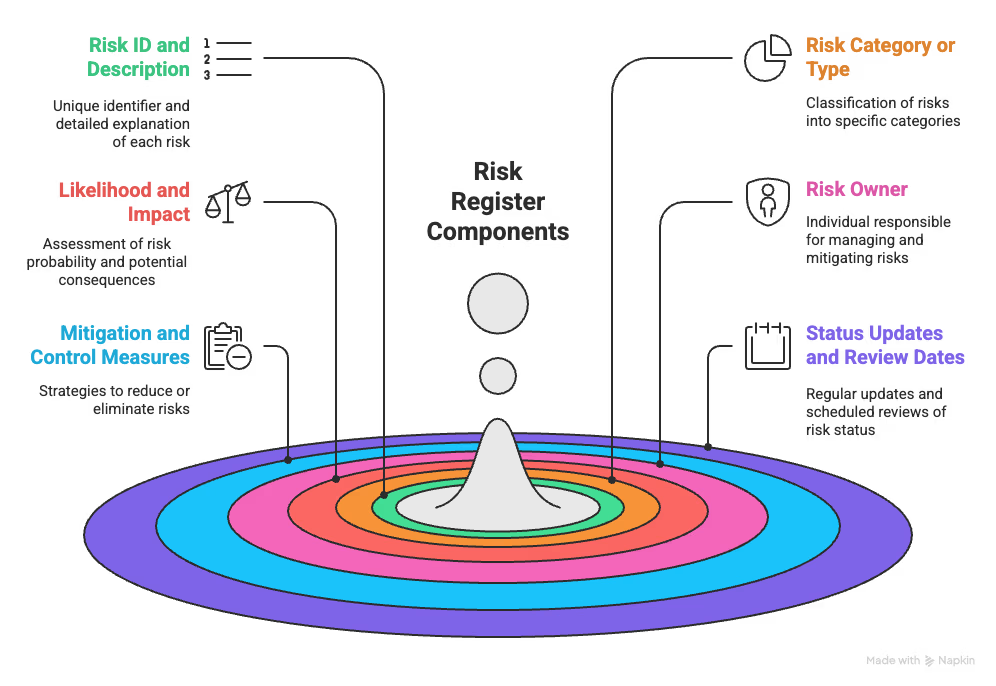
Risk Register Components
Each component is critical to building a risk management framework that actually works.
Every risk gets a unique identifier—R-001, RISK-2024-01, or similar. The description should answer three questions: What could go wrong? What triggers it? What happens if it hits? Clear descriptions ensure everyone interprets the risk the same way, reducing miscommunication. This is the foundation for understanding and prioritizing threats.
Categories show who should care about each risk. Common types include:
Consistent categories help spot patterns, assign responsibility efficiently, and make risk tracking systematic and actionable.
Assess the probability and potential impact of each risk. Most teams use a 1–5 scale. Multiply likelihood × impact to calculate a risk score, highlighting the most critical risks. This helps prioritize threats and guides resource allocation to reduce project disruption.
Every risk must have a single accountable person—not a committee. This individual monitors the risk, executes mitigation plans, and keeps stakeholders updated. Clear ownership ensures accountability and prevents risks from being neglected.
Decide how each risk will be addressed: reduce it, monitor it, protect against it, or transfer it. Document the strategy clearly. Well-planned mitigation turns risks from threats into manageable challenges.
A risk register dies if ignored. Track current status, review dates, changes, and the effectiveness of mitigation. Regular updates keep it alive, actionable, and relevant, turning a static document into a dynamic management tool.
Get these six components right, and your risk register becomes a practical, living tool—not just another document gathering dust.
Want to see what actually works? Here are three real scenarios that show up in risk registers everywhere. No theory—just practical examples you can adapt.
Vendors will fail you—not because they’re evil, but because they’re human.
Risk ID: R-001
Description: Key supplier fails to deliver critical components on time due to labor shortages
Impact: 3–4 week project delay, potential penalties
Likelihood: Medium (50%)
Priority: High
Owner: Supply Chain Manager
Mitigation: Identify alternate suppliers, buffer timelines, expedite partial shipments
Pro tip: nearly 25% of all data breaches originate from vendor issues. Treat vendor dependencies seriously. Ask tough questions: performance history, culture alignment, competency, capacity. And document your change control process—undocumented changes kill projects faster than bad weather.
Large IT projects run 45% over budget on average. Shocking? Not really.
Risk ID: R-002
Description: Scope changes causing budget overruns
Impact: Increased costs, reduced ROI
Likelihood: High
Priority: High
Owner: Project Manager
Mitigation: Implement change control, document requirements thoroughly
Scope creep sneaks in via inaccurate requirements, undocumented requests, poor change management, or fantasy labor estimates. Spell out exactly how changes get approved and what they’ll cost—no exceptions.
Cyber threats are a different beast.
Risk ID: R-003
Description: Credential compromise via phishing
Impact: Loss of organizational accounts
Likelihood: Medium
Mitigation Cost: 100 hours
Mitigation: Deploy phishing detection software
Cyber risk registers need special categories: data protection, cloud security, access management. Track common threats: data leaks, mobile media risks, vendor network compromises. Quantify mitigation efforts in hours or dollars—it makes the risk real.
Project managers who ignore risk management? They’re basically gambling with failure. Every project needs a project management risk register to track potential issues, assign ownership, and guide teams through uncertainties. Skip it, and your project crashes—it’s that simple. But here’s what most people miss: a risk register isn’t busywork. It’s the difference between steering through uncertainty and getting blindsided when things blow up.
Here’s a hard truth: a four-year study of 35 large projects found nearly half of all risks weren’t detected until after they caused damage. That’s not just bad luck—it’s bad management. Teams were reacting instead of preparing.
A working risk register flips the script. It gives you:
It’s not about filling in boxes—it’s about building foresight into the way you run projects.
Start early—during project planning—when you still have room to act instead of react. A risk register built late is just damage control. Using a risk register project management approach ensures risks are identified and mitigated systematically rather than reactively
Step 1: Hunt down risks. Bring the team together and list every possible threat: technical failures, vendor delays, compliance issues, budget creep. Nothing is too small to note.
Step 2: Rate them honestly. Use a high/medium/low scale or numbers. Multiply likelihood × impact to see which threats deserve your attention first.
Step 3: Plan your response. Decide if you’ll reduce the risk, monitor it, transfer it elsewhere, or accept it. Write the plan in plain language—no vague promises.
Step 4: Assign ownership. Each risk needs a single accountable person who tracks progress, acts quickly, and keeps updates flowing.
A register that isn’t updated is already dead. Keep it alive with:
Your risk register should live inside your project workflow—not in a forgotten folder. When it’s active, it’s not paperwork. It’s your survival map through uncertainty.
A cybersecurity risk register is a living document that catalogs, ranks, and tracks every digital threat that could compromise your systems, data, or operations. Maintaining a risk register cyber security is essential for tracking vulnerabilities, mitigation strategies, and ensuring compliance across your organization. Think of it as your playbook against attackers—a clear map of where you’re exposed and how you’ll respond.
Standard project risk registers move too slowly for cyber threats. A new exploit can appear overnight, reshaping your attack surface before morning coffee. Cyber registers need real-time threat intelligence, deeper technical insight, and constant updates to stay relevant. They also align with frameworks like NIST, ISO, or GDPR, ensuring regulatory compliance while guiding actionable defense strategies.
These registers go beyond generic ones, logging:
They’re also proof to regulators, boards, and customers that risks are actively managed—not just internally tracked.
Every serious cyber register should cover:
Maintaining these registers requires effort. Done right, they let you prioritize spend, harden defenses, and stay ahead of evolving threats—turning reactive security into a proactive strategy that actually works.
The wrong software will kill your risk management efforts. Period. A bloated platform slows everyone down. A barebones one leaves you exposed. You need something that matches your team’s size, complexity, and maturity.
Here are four tools that consistently stand out:
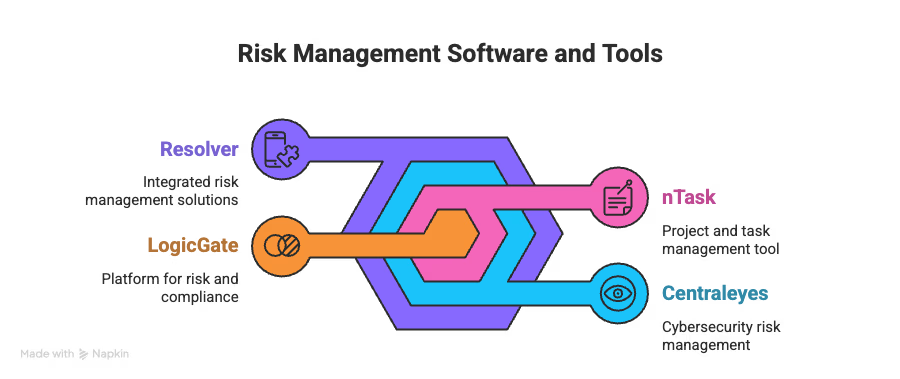
Risk Register Software and Tools
Let’s get into each of these and see what makes them tick.
Want pretty risk maps? LogicGate Risk Cloud delivers. This platform lets you build custom risk registers that actually fit your business instead of forcing you into someone else’s template.
Why it stands out:
Users rate it high (4.6/5 on G2, 4.7/5 on Capterra) because it’s flexible. The downside? It has a steep learning curve, and some teams stumble through the interface early on.
If you’re already juggling multiple projects, nTask bakes risk management directly into project workflows. It treats risks as part of getting the job done, not an extra chore.
Why it stands out:
It’s solidly rated (4.4 on G2, 4.2 on Capterra). Users love the intuitive design and responsive support. The con? It can lag under heavy workloads.
For enterprises that need strict control, Centraleyes shines. It’s a SaaS platform designed to make compliance and risk mapping less painful.
Why it stands out:
It’s automation-heavy without stripping away manual oversight, which is rare in this space.
Built for mid-size to enterprise, Resolver focuses on context-driven risk profiles.
Why it stands out:
It scores well (4.4/5 on G2 and Capterra). Reviewers highlight its clean interface and strong support team.
Bottom line: Match the tool to your needs. Don’t buy enterprise horsepower for a small team problem.
Creating a risk register is only step one. The real work is keeping it alive and useful. Most managers let these documents rot in a folder—don’t be that person. Without proper care, even the most detailed register is just digital clutter.
Your risk landscape evolves constantly. If you’re updating only annually, you’re already behind. Smart organizations review quarterly—or sooner when:
Vague descriptions kill projects. Use the “Cause-Risk-Effect” method—clear cause, clear effect, no guessing. Build a strong category framework (operational, financial, compliance), assign every risk, and use categories to spot trends.
Visual grids cut through the noise, showing which risks matter most:
Your register can’t live in isolation. Connect it to your workflow to get:
Bottom line: a risk register is only as effective as the attention you give it. Treat it like the critical business tool it is.
Here’s the reality: you can keep gambling with your projects, or you can start using tools that actually work. Smart organizations don’t leave success to chance—they document risks, assign ownership, and have clear plans for when things go sideways. And make no mistake—they will.
The best risk registers aren’t static—they’re living, breathing tools. They evolve as priorities shift, new threats emerge, and projects grow. High-performing teams do four things differently:
Cybersecurity risks? That’s a whole different beast. They demand faster updates, deeper technical detail, and alignment with regulations. Using the right software—LogicGate, nTask, Centraleyes, Resolver—makes this infinitely easier and keeps your team ahead of threats.
Here’s the uncomfortable truth: every day you delay is another day flying blind. Your competitors aren’t waiting, threats aren’t pausing, and stakeholders expect you to know what’s coming.
The choice is yours: keep hoping, or start preparing. Your future self will thank you.
Take control of compliance, reduce risk, and build trust with UprootSecurity — where GRC becomes the bridge between checklists and real breach prevention.
→ Book a demo today

Senior Security Consultant