0%
Ever wondered who’s been snooping around your digital files? Or why a system crashed last Tuesday at exactly 3 PM?
In today’s digital-first world, every action leaves a trace. Every login, file edit, access request, or failed attempt quietly drops a breadcrumb. Individually, they seem harmless. Together, they tell a story. That story is your audit trail.
Modern systems don’t just process data — they remember it. Who did what. When it happened. Where it came from. And how it was done. Whether it’s a finance team updating payroll, a developer pushing code, or a nurse opening a patient record, every interaction creates a permanent digital footprint.
Organizations rely on these records more than ever. In fact, nearly a third already depend on in-app audit systems to understand user behavior and catch privacy issues before they spiral into breaches.
Audit trails aren’t background noise. They’re the difference between guessing what happened and knowing — with proof. And as regulations tighten and threats grow smarter, that difference matters more than ever.
An audit trail is a chronological, tamper-resistant record of activities within a system. Think of it as a security camera for your digital operations — always on, always watching. Knowing the audit trail meaning shows why these logs are crucial for tracking every system action.
A strong audit trail captures the full picture: who performed an action, what they did, when it happened, where it originated from, and how it was executed. These records are automatically logged and stored securely, creating an unbroken chain of evidence that can’t be altered after the fact.
Why does this matter? Because when something goes wrong — and eventually it will — audit trails turn chaos into clarity. They help organizations investigate incidents, detect fraud, prove compliance, and hold users accountable.
They also act as a deterrent. When people know their actions are traceable, risky behavior drops. From financial reporting to healthcare privacy to GDPR compliance, audit trails aren’t just helpful — they’re foundational to trust, security, and operational integrity.
Different industries, different rules. Different risks, different consequences.
You can’t track a hospital’s patient records the same way you monitor a bank’s payroll system. Each industry uses audit trails differently, shaped by regulations, threat models, and the kind of damage a single mistake can cause.
Healthcare doesn’t get room for error. One slip with patient data can trigger lawsuits, regulatory penalties, and real-world harm.
That’s why EHR audit trails are extremely detailed. They track:
HIPAA requires these logs to be retained for at least six years. More importantly, they must be tamper-proof. Once recorded, they can’t be altered or erased.
Because in healthcare, “the logs were missing” is never an acceptable excuse.
Software audit trails act like a security guard that never looks away.
They log:
These logs aren’t just for catching malicious behavior. They’re critical when systems fail. When apps crash or data disappears, audit trails reveal whether it was user error, misconfiguration, or a system fault.
Without it, you’re guessing. And guessing doesn’t scale.
When money is involved, audit trails become non-negotiable.
Payroll systems track:
This isn’t overkill. It’s protection. When salaries are delayed, misrouted, or altered, audit trails provide answers — fast. Employees trust their paychecks to be right. Audit trails are how you prove they are.
This is where audit trails turn critical.
Security-focused audit trails monitor:
When breaches happen — and they do — these logs become forensic evidence. They show how attackers got in, what they touched, and where defenses failed.
Without detailed audit trails, security teams are flying blind in a threat landscape that keeps getting smarter.
Most people think audit trails just happen — like magic. They don’t. Behind every clean log and investigation-ready record is a deliberate, end-to-end process designed to ensure nothing slips through the cracks. No mystery. No guesswork. Just method.
These are the core steps that make an audit trail work:
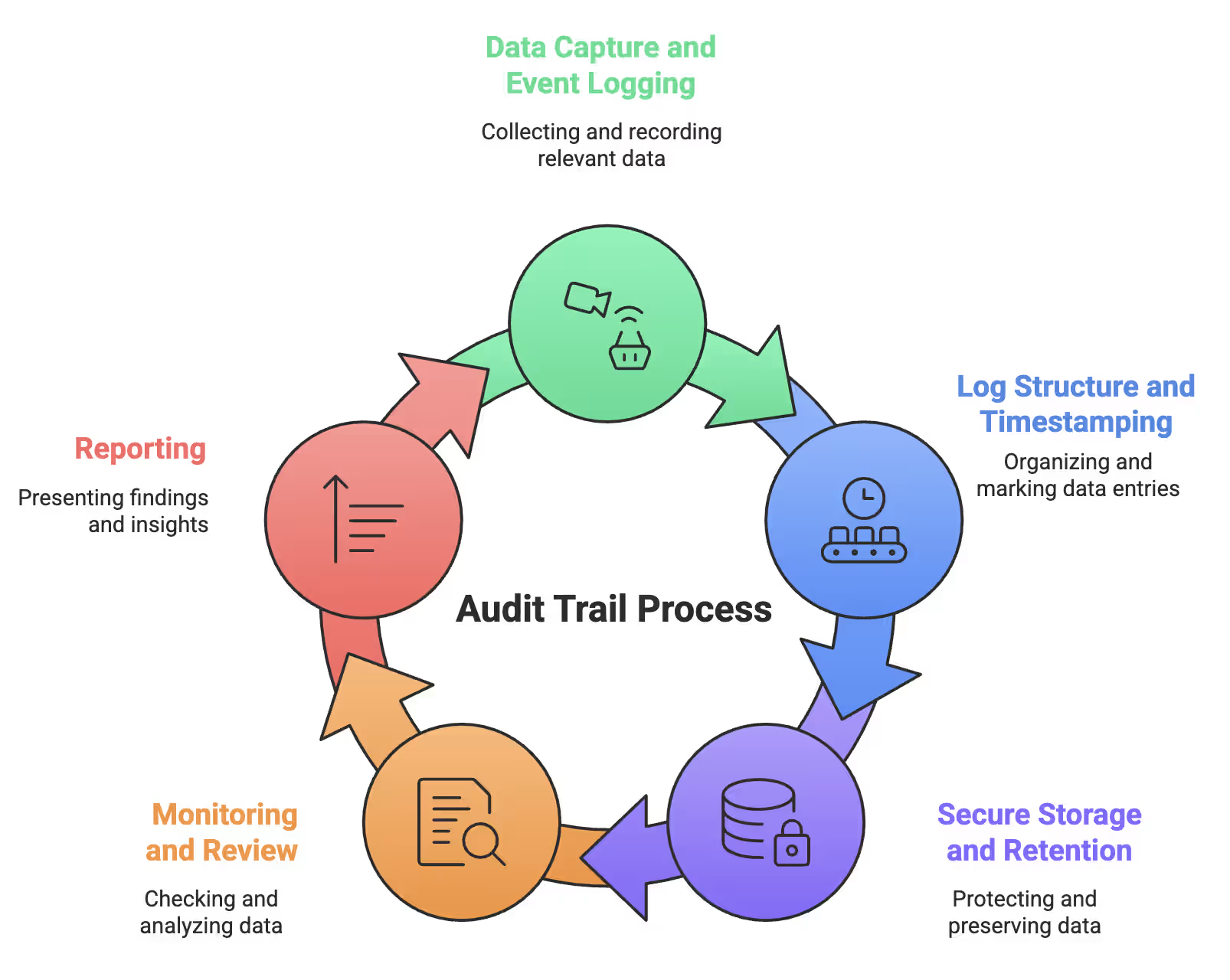
Audit Trail Process
Let’s get into the steps.
The moment an action happens — a login, file edit, deletion, or failed access attempt — the system records it automatically. No human input required.
Think of it as an assistant that never blinks. Every interaction triggers an event log in real time.
Most systems capture:
Some environments go deeper, tracking command execution or system responses. It may feel excessive — until you’re investigating suspicious activity and need every detail.
Raw data is useless without structure.
Each audit record follows a consistent format that answers four critical questions:
Accurate timestamps are non-negotiable. Systems synchronize clocks using Network Time Protocol (NTP). Without synced time, even minor drift can break incident timelines and investigations.
Once captured, audit data must be locked down.
Retention rules vary — healthcare logs often require six years, financial systems closer to seven — but one rule never changes: logs must be tamper-proof.
Organizations protect audit data using:
If audit logs can be altered, they can’t be trusted.
Capturing logs is only the beginning. What matters is what you do next.
Modern systems generate massive volumes of audit data, making manual review impractical.
Instead, automated monitoring flags issues like:
This turns raw logs into actionable insight — helping teams detect issues early and support investigations, audits, and compliance reporting.
Regulations aren’t suggestions — they’re the law. Audit trails are no longer optional. Miss documentation requirements, and fines, penalties, or worse could sink your company. Strong audit trails turn compliance from a headache into verifiable proof of accountability.
GDPR made data privacy a serious business. Organizations must maintain precise records of all personal data processing:
GDPR doesn’t mandate exact logging methods but stresses accountability — something audit trails deliver perfectly. Logs must be stored securely for required periods and protected from tampering.
Healthcare organizations handling ePHI face strict HIPAA rules:
Retention? At least six years, sometimes longer. Access? Restricted to authorized IT personnel only.
Sarbanes-Oxley enforces accountability for public companies:
Penalties for falsifying records? Up to $5 million in fines and 20 years in prison.
The benefit: solid audit trails simplify audits, provide strong legal defense, and demonstrate operational excellence. Companies that master them don’t just stay compliant — they gain trust from regulators, investors, and customers alike.
Audit trails aren’t just compliance boxes — they’re business superpowers disguised as logs. They help detect fraud, improve accountability, streamline audits, and protect data integrity.
Scare fraudsters by showing you’re watching. Every login, file access, and transaction leaves a permanent footprint. Audit trails spot suspicious logins, unusual transaction patterns, and changes to sensitive systems. Employees think twice when their actions are recorded. The audit trail silently prevents issues before they escalate, protecting against internal and external threats.
Audit trails create a transparency-driven workplace. When people know their actions are documented, they naturally follow rules. Mistakes happen — but logs point directly to what occurred and who was responsible. No finger-pointing. No excuses. Clear accountability makes teams more responsible and organizational operations more reliable and trustworthy.
Audits don’t have to be painful. Well-structured audit trails cut review times by up to 40%, freeing hours for actual business work. Legal challenges? Logs act as a digital lawyer, providing unchangeable, objective evidence of exactly what happened and when. They simplify compliance reporting, strengthen internal controls, and offer proof during disputes, giving organizations confidence under scrutiny.
Audit trails act as insurance for your data. Crashes, hacks, or server failures? Logs help rebuild systems quickly. They reveal vulnerabilities early, preventing small issues from becoming major disasters. Complete audit records maintain data integrity, operational resilience, and uninterrupted business continuity.
Audit trails aren’t just about avoiding problems — they turn routine logs into essential tools for smarter, safer, and more accountable business operations.
Ready to set up your own digital detective? Implementing an audit trail system isn’t rocket science, but it’s not plug-and-play either. Most organizations either log everything (hello, storage costs!) or too little, missing critical events. The key is balance: capture essential actions without drowning in noise and ensure your logs remain actionable, readable, and tamper-proof.
Don’t rely on polished demos alone. Focus on essentials:
Pro tip: Ask vendors to demonstrate real-world handling of edits, overrides, and specification changes. Organizations with standardized systems reduce review times by up to 40%, making the upfront effort worthwhile.
Every user needs a unique account. Shared logins make audit trails nearly useless.
Real-time monitoring using User Activity Monitoring (UAM) tools detects suspicious patterns instantly. Waiting until a monthly review is like closing the barn door after the horse has bolted.
Audit trails must cover your entire tech stack — cloud, on-premises, and hybrid environments. Centralized logging provides a unified view across platforms.
Checklist for integration:
Integration takes longer than most expect, but done right, it creates an end-to-end, tamper-proof audit trail that defends against internal and external threats, simplifies audits, and provides full operational visibility across your organization.
Time for some real talk. These aren’t theoretical boardroom scenarios — these are actual situations where audit trails saved the day, caught someone red-handed, or prevented costly mistakes before they escalated. Understanding these examples makes it obvious why audit trails aren’t optional.
QuickBooks tracks nearly everything. Both Desktop and Online versions log:
Smartly, QuickBooks creates system profiles like “Online Banking Administration” and “System Administration” to track automated changes. This gives full visibility even when robots or background processes make changes, ensuring nothing slips through unnoticed.
Web apps act as digital detectives, capturing:
These logs are more than compliance tools — they’re essential for troubleshooting. When something goes wrong, the audit trail allows teams to reconstruct exactly what happened and determine whether it was human error, a misconfiguration, or a system failure.
Audit trails are heroes in finance:
A controller spotted a $50,000 revenue entry posted incorrectly and corrected it before financial statements went out
An accounts payable manager identified a deleted $3,200 vendor payment, preventing a payroll disaster
During an IRS audit, a small business used its audit logs to prove all transactions were legitimate, satisfying the auditor immediately
Think of audit trails as digital receipts. They prove who did what, when, and where — except unlike paper receipts, these never fade, get lost, or go missing. They create permanent, verifiable records that keep your systems accountable and your business protected.
Audit trail technology isn’t standing still. Companies are already building the next generation of tracking systems that make today’s tools look ancient. AI and machine learning are becoming standard — 83% of businesses plan to invest more in automated audit solutions.
The future is clear:
Understanding audit trails isn’t optional. Regulations tighten, penalties soar, and small businesses remain vulnerable — 76% of cyberattacks target companies under 250 employees.
The good news? Cloud-based audit solutions are cheaper and more powerful every day. Audit trails aren’t just keeping pace — they’re leading the charge in security, compliance, and operational trust.

Senior Security Consultant