0%
Ever wonder why some companies get hacked while others sail through unscathed? It’s not luck. It’s planning.
Here’s the harsh reality: cyber attacks are expensive. Globally, the average data breach cost hit USD 4.88 million in 2024—up 10% from 2023. And it’s not just outsiders you need to worry about. Employees are responsible for 43% of data loss, often without even realizing it. Ignored security rules? That’s when 74% of organizations end up breached.
Regulations aren’t optional either. Industries like healthcare, finance, and telecom face hefty fines if security measures aren’t followed. And reputation? One breach can erase years of customer trust.
Small business owners, take note: you don’t need a 200-page manual to stay safe. Even a few well-crafted pages can create consistency across your team, define responsibilities, and ensure your security budget is spent wisely. Firewalls and antivirus software won’t save you if your people don’t know the rules.
Planning ahead is the first step to staying secure—and that’s where your cyber security policy comes in.
If you’ve ever asked what is cyber security policy, it’s your company’s rulebook for protecting digital assets and managing risks. It’s more than just paperwork—it’s the backbone of your defense strategy. A strong cyber security policy outlines how your organization secures customer data, internal systems, and everyday operations.
A strong policy matters because it:
Without a cyber security policy, even the best tools can’t protect your business. It’s not optional—it’s your strategy for surviving—and thriving—in a world full of digital threats.
Not all cyber security policies are the same. Experts generally break them into three main types—organizational, system-specific, and issue-specific—each serving a clear purpose. For small businesses, these same policies can be simplified to focus on essentials without losing protection The right policies ensure your business is prepared for threats and that everyone knows exactly what to do when something goes wrong.
Organizational policies are your master plan. They:
System-specific policies focus on the details. They cover:
The hierarchy is simple: senior management sets the organizational policies, and system-specific rules flow down to keep everyone aligned. This structure prevents gaps, ensures consistency, and makes it easier to enforce rules across all teams.
Some areas need special attention. Email is the top attack vector—78% of organizations faced email-based ransomware in 2021. Policies guide:
BYOD policies protect personal and work data on employee devices, covering device security, access controls, and login requirements. Internet use policies set clear boundaries for online behavior, helping prevent misuse—26% of organizations have even fired staff for violations.
Small businesses are frequent targets—43% of cyber attacks hit them. But your cyber security policy for small business doesn’t need to be a long, complex document. Focus on essentials:
Even with limited resources, these simple policies cut risk significantly. Start small, enforce consistently, and expand over time. Building these habits creates a security-focused culture that protects your data, your people, and your reputation.
Building an effective company cyber security policy isn’t rocket science—but it requires the right ingredients to actually protect your business. A strong policy turns paperwork into real defense, guiding your team on what to do before, during, and after incidents. It sets expectations, assigns responsibilities, and ensures everyone understands the rules so your organization can operate securely and confidently.
This is where you set the tone. Keep it simple and clear—skip corporate jargon. A strong statement should:
This statement becomes the foundation of your security culture, shaping how all other policies are applied.
Clarity is critical. Define exactly:
No gray areas—everyone must know what’s in scope.
Security fails when roles aren’t clear. Responsibilities should include:
Clearly defined roles enable faster, coordinated responses when incidents occur.
Your policy should cover essential technical controls:
Incidents will happen. Your plan should include:
A solid cyber security policy assumes something will go wrong and prepares everyone to respond effectively. It combines clarity, defined roles, strong controls, and planning—creating a framework that protects your business, your people, and your reputation.
Time to roll up your sleeves. Building a solid cyber security policy isn’t rocket science, but it does need a plan. Follow these steps to create a policy that actually protects your business and keeps your team aligned:
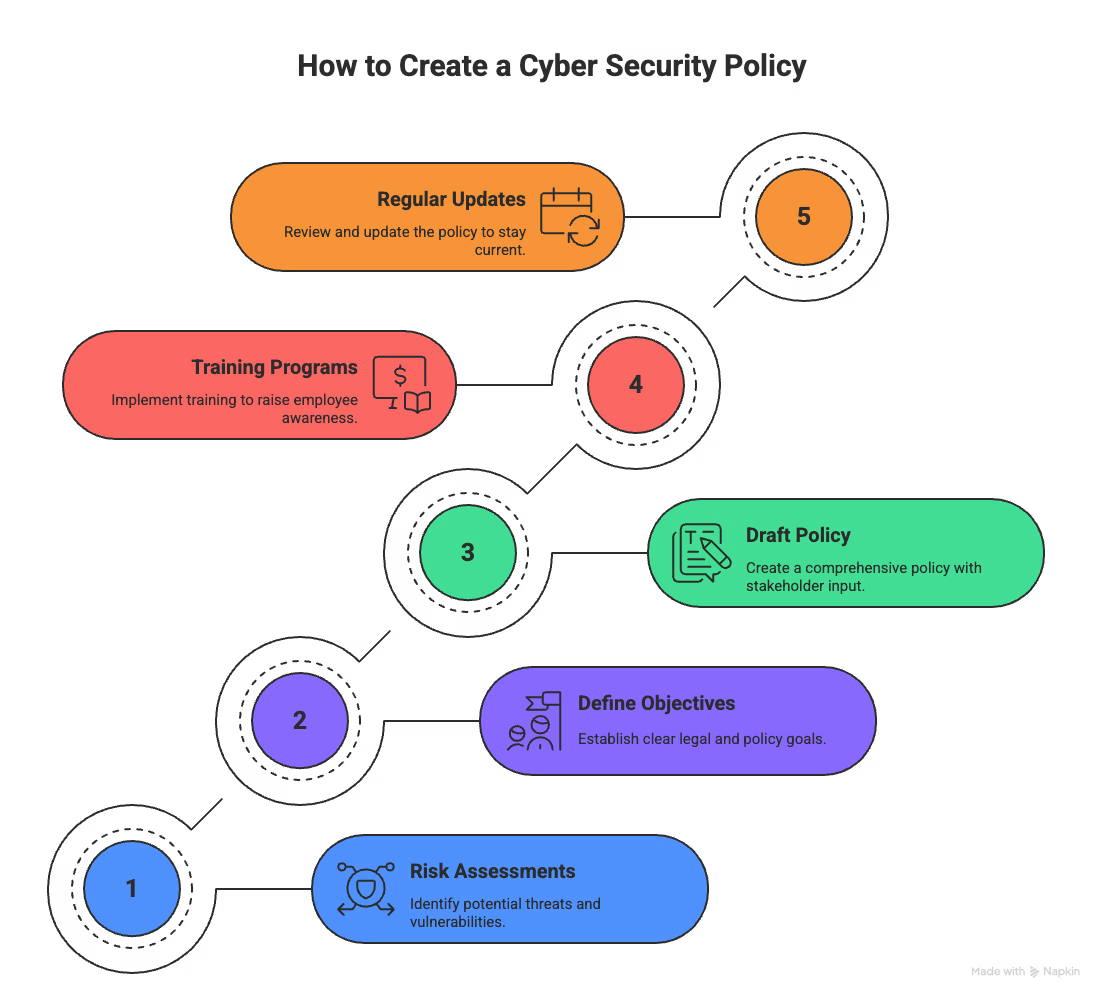
How to Create a Cyber Security Policy
Let’s get into each of these steps in detail:
Before you can defend anything, you need to know what you've got. Start with a proper risk assessment:
Don’t just tick boxes here. You need the full picture. Organizations that involve stakeholders in mapping risks often discover blind spots they wouldn’t see otherwise.
Every business must follow certain rules. Depending on your industry, these might include:
Rules change frequently—26% of organizations update their cyber security policy and procedures every year to stay compliant.
Your policy works best when multiple perspectives contribute:
The best policy in the world is useless if nobody follows it:
A policy isn’t “set it and forget it”:
Follow these steps and you’ll have a cyber security policy that protects your business, ensures compliance, and keeps your team ready for real-world threats.
A cyber security policy sitting in a drawer won’t stop hackers. The magic happens when you actually implement it. Most companies fail here — they write solid policies, then wonder why breaches keep happening.
Your policy only works if people follow it. That means keeping an eye on compliance without creating fear:
Reality check: the average business juggles 75 security tools. Chaos. Smart companies use automated compliance monitoring with real-time dashboards — no guessing games.
Your cyber information security policy must align with your systems:
When policy and technology work together, you get transparency, trust, and smoother operations.
Policies gather dust unless they become habit. Explain the “why” behind rules, lead by example — executives first — and train regularly on new threats, not just during onboarding. The goal: your policy stops being a document and becomes company DNA. Regular training reduces breach risk from human error.
Implementation is what separates companies that talk about security from companies that actually stay secure.
Why reinvent the wheel when experts have already built it for you? The right sample cyber security policy template can save weeks of work, and many top organizations share them for free.
Skip generic templates online. These sources actually know what they’re doing:
For small businesses, these are goldmines — especially if you don’t have a dedicated security team or a big budget.
Templates are like store-bought cake mix — a good base, but you need your own ingredients. Customize for your business:
Copy-paste won’t cut it. Remember: 43% of all cyber attacks target small businesses.
Cyber information security policy examples include:
CIS alone offers 15+ specialized templates covering malware defense, vendor management, and more. Pick what fits, build from there, and make your policy practical. Start simple, make it real, and your business will be safer for it.
Cyber security policies aren't like fine wine. They don't get better with age if you just let them sit there.
Here's the uncomfortable truth: your shiny new policy becomes useless the moment you stop paying attention to it.
Your policy in cyber security needs constant care because hackers don't take breaks:
The rule makers never sleep:
Stop treating policy updates like a chore. Make them work for you:
The real goal? Make security so natural in your company that employees follow good practices without even thinking about it. Strong policy cybersecurity keeps your defenses aligned with evolving threats, ensures compliance, promotes accountability, and fosters a culture of continuous improvement.
Your cyber security policy for company only works when it becomes part of how people actually work—not just another document gathering dust.
Here’s the truth — cyber security policies aren’t paperwork. They’re armor. And if you think only big companies get hacked, think again. Forty-three percent of cyber attacks target small businesses, and the average breach costs $4.88 million in 2024. Prevention is cheaper. Always.
What really makes a policy work comes down to three things:
The real failure isn’t bad policy. It’s policy nobody follows. Make it culture, not paperwork. Review often, train regularly, and make sure leadership backs it. You don’t need a 100-page manual — just a few strong pages everyone understands and actually uses.
Cyber threats move fast, so start now, stay ready, and protect what you’ve built. Because yesterday was the best time to begin, and the second-best is today.
Take control of compliance, reduce risk, and build trust with UprootSecurity — where GRC becomes the bridge between checklists and real breach prevention.
→ Book a demo today

Senior Security Consultant