0%
Your security team is overwhelmed—and the numbers don’t lie. More than half of IT and GRC professionals have experienced a breach in the last 24 months, while most are still stuck managing risk manually. The solution isn’t just more staff—it’s automation in risk management. That’s not a skills problem. It’s a systems problem.
Every day, over 100 new CVEs are disclosed. Attackers don’t wait. They begin scanning for exposed systems within hours, while many organizations still rely on quarterly patch cycles. The result is a widening gap between how fast threats move and how slowly risk is managed.
The situation worsened after COVID. Rapid digitization expanded attack surfaces overnight, but security teams didn’t grow at the same pace. Manual processes couldn’t scale then—and still can’t today.
Modern risk management isn’t about working harder. It’s about working smarter with systems built for speed, scale, and visibility. Organizations that fail to modernize how they assess, monitor, and respond to risk aren’t inefficient—they’re exposed. Automation stops being optional and starts becoming essential today.
Manual risk management isn’t just slow—it’s dangerous. The moment a manual assessment is completed, it’s already outdated. Without continuous monitoring, threats slip through unnoticed. Repetitive tasks drain skilled professionals, increasing errors and burnout, while siloed data creates blind spots across teams.
Automation changes the equation. Organizations that replace manual processes see a 40–60% reduction in assessment time and significantly higher returns on security investment. Automated systems operate continuously, monitoring environments 24/7, triggering real-time alerts, and responding the moment risks emerge.
AI-powered automation goes further by identifying patterns, prioritizing threats, and predicting potential exposures before they turn into incidents. Instead of chasing alerts or updating spreadsheets, security teams can focus on strategy, remediation, and resilience.
Modern threats demand modern defenses. Automated risk management enables speed, accuracy, and scale—capabilities manual processes simply cannot deliver in today’s threat landscape.
Effective automation isn’t about piling on tools and hoping for results. Strong risk management automation systems are built from connected components that work together to identify, assess, monitor, and respond to risk across the organization. Many organizations achieve this using GRC automation tools that centralize workflows and risk data. Each element plays a specific role—and missing one weakens the whole system.
At a high level, these systems rely on five core elements:
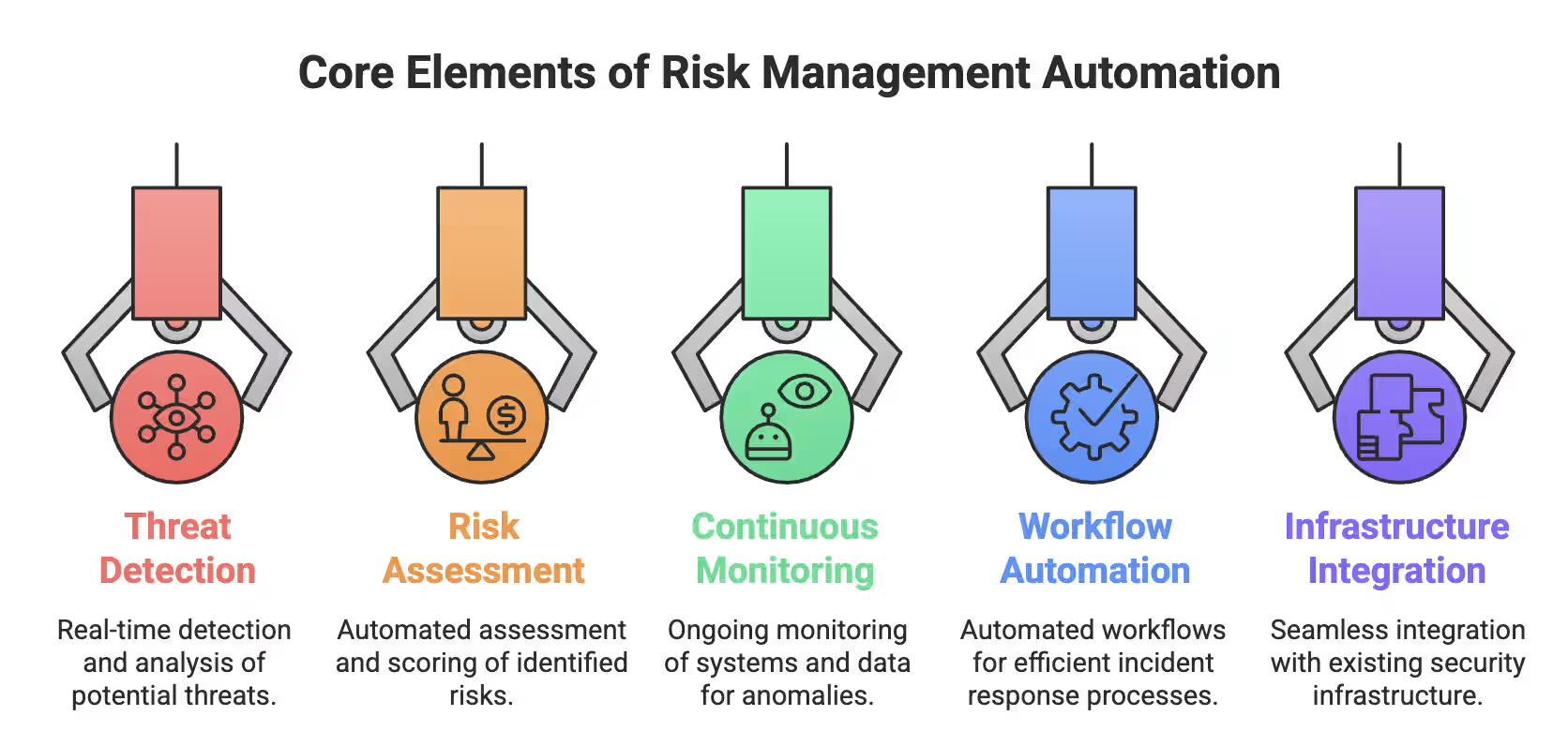
Core Elements of Risk Management Automation
Let’s break down how each of these components actually works in practice.
Modern threat detection uses AI and machine learning to continuously analyze massive volumes of security data without human fatigue. These systems focus on:
High-risk activity triggers automated responses such as endpoint isolation, IP blocking, or additional authentication, stopping threats before they escalate.
Automated risk assessment tools evaluate threats based on likelihood and business impact, eliminating subjective judgment. They work by:
This ensures risks are prioritized accurately and assessed uniformly across the organization.
Point-in-time assessments become outdated quickly. Continuous monitoring delivers real-time visibility by:
Teams can respond dynamically instead of reacting after damage is done.
Incident response automation standardizes detection, investigation, and remediation through predefined playbooks. These workflows:
This removes inefficiencies caused by manual alert handling.
Effective automation depends on seamless integration. Strong platforms:
This unified view enables faster, coordinated, and more effective risk response.
Automating risk management changes how security teams operate. It replaces reactive, manual processes with systems designed to scale, adapt, and stay current as threats evolve.
Automation eliminates repetitive work that drains security teams. Risk data updates continuously, inputs from multiple tools are consolidated automatically, and reports generate without manual effort. Organizations typically see a 40–60% reduction in time spent on routine assessments, freeing teams to focus on remediation and strategy instead of documentation.
Manual risk tracking struggles with volume and complexity. Automated systems use machine learning and behavioral analysis to identify patterns humans miss. Continuous monitoring reduces blind spots, cuts false positives, and surfaces real threats earlier—improving detection accuracy while reducing alert fatigue.
Automation enables smarter prioritization by scoring risks based on likelihood and business impact. Teams stop treating every issue as equally urgent and focus resources where they reduce the most risk. This leads to better use of security budgets, fewer disruptions, and stronger overall resilience.
Compliance shifts from last-minute panic to continuous readiness. Automated tools track regulatory changes, map controls, and highlight gaps early. Audit preparation becomes faster, less disruptive, and significantly cheaper, without pulling teams away from security operations.
Automation turns raw risk data into clear dashboards, heatmaps, and trends. Security leaders gain real-time visibility into risk posture and can justify decisions with data—not gut instinct. This clarity improves alignment across teams and enables faster, more confident decision-making.
Automation isn’t something you switch on. It’s something you implement deliberately. With more than half of risk leaders increasing automation spend, the difference between success and shelfware comes down to structure, not tools.
Effective automated risk assessment follows a clear sequence:
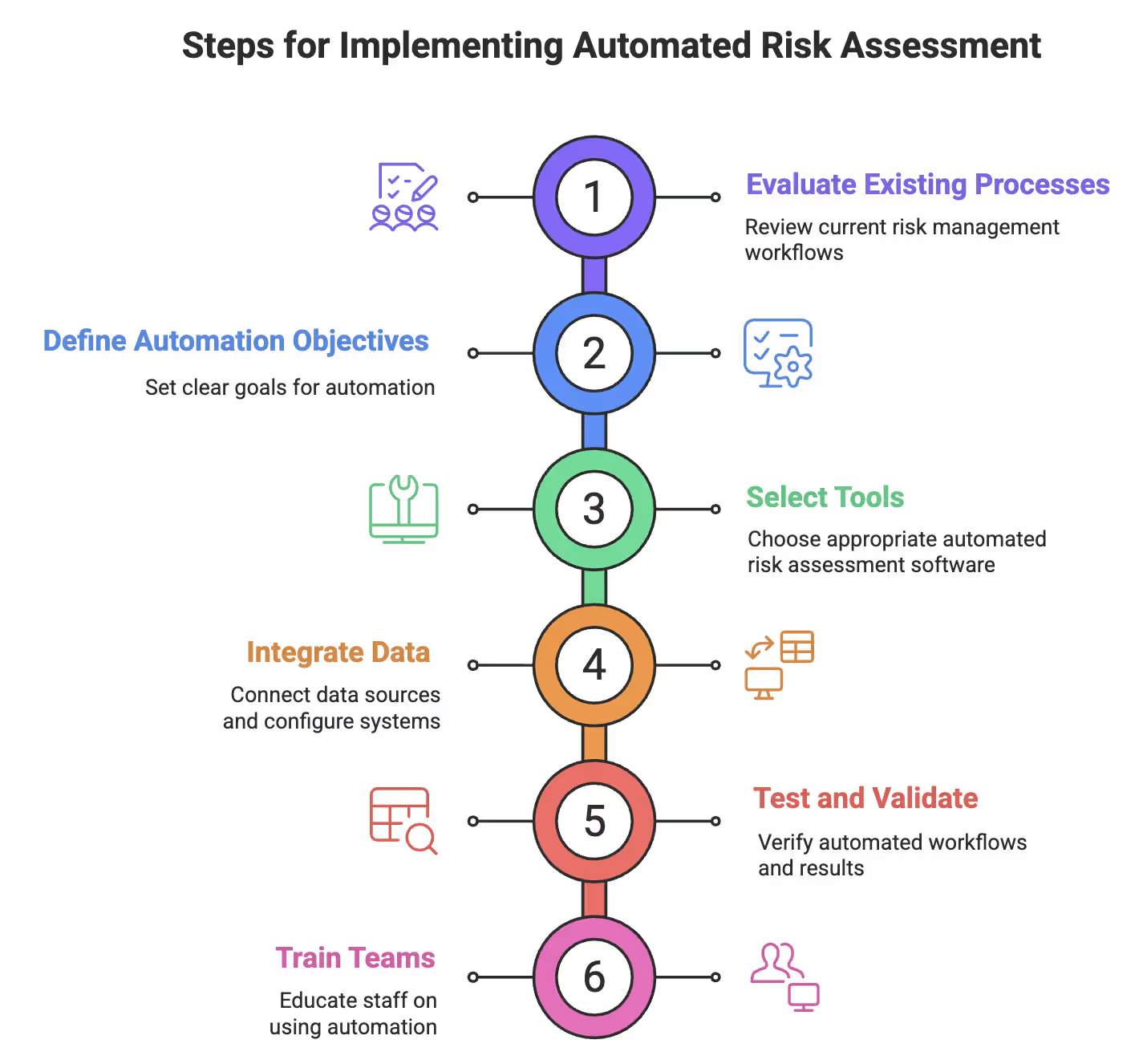
Steps for Implementing Automated Risk Assessment
Let’s break down what each step involves.
Start by taking a hard look at how risk is managed today. Map end-to-end workflows, identify manual handoffs, and document where data is fragmented, delayed, or outdated. Spreadsheet-driven processes rarely scale and often conceal critical risk gaps as the organization grows. This step establishes a clear baseline, ensuring automation improves existing practices instead of reinforcing broken ones.
Automation only works when success is clearly defined. Set measurable objectives such as reducing assessment cycles, expanding continuous monitoring, or improving enterprise-wide risk visibility. Be explicit about which activities will be automated and where human oversight remains essential. Clear goals keep automation focused on outcomes, not just activity.
Choosing tools is about alignment, not features. Evaluate platforms based on scalability, integration support, configurability, usability, and regulatory fit. The right solution should adapt to your environment and workflows, not force teams to change how they operate just to fit the tool.
Automation depends on accurate, connected data. Integrate cloud platforms, identity systems, security tools, and business applications using APIs. Configure rules to correlate signals against defined risk thresholds so assessments remain current and context-aware. Poor integration is the fastest way to undermine automation value.
Never skip testing. Validate individual components, end-to-end integrations, user workflows, and compliance logic before rollout. Early testing uncovers gaps, misconfigurations, and false assumptions—issues far cheaper to fix before automation goes live.
Automation succeeds when teams trust it. Train staff to interpret outputs, understand limitations, and apply judgment where context matters. The goal is augmentation, not replacement—automation handles scale, humans handle decisions.
Automated risk assessment works best when implemented step by step. Done right, it improves visibility, speeds decisions, and allows risk management to scale as threats evolve.
Automation sounds perfect—until it isn’t. Even the slickest risk management tools can backfire if implemented poorly. Understanding common pitfalls and planning safeguards is critical to capturing the benefits without creating new vulnerabilities.
Automation is powerful, but blind trust is dangerous. Many teams assume systems catch everything—they don’t. Human oversight often disappears, expertise atrophies, and zero-day threats slip through unnoticed.
Mitigate this by dividing responsibilities clearly: let automation handle repetitive, data-heavy tasks, while humans make judgment calls. Conduct regular exercises that throw unexpected scenarios at your systems to ensure teams remain sharp and capable.
Security teams often get flooded with hundreds of alerts daily, most of which are false. Important events can get buried in the noise, delayed responses occur, and cognitive overload leads to burnout.
Address this by tuning alerts, adding severity ratings, and defining precise response protocols. Prioritize actionable alerts so teams can focus on genuine threats efficiently without being distracted by irrelevant noise.
Automation magnifies bad data. Missing metadata, inconsistent standards, entry errors, and siloed systems create errors that propagate quickly and undermine trust in automated assessments.
Fix this with standardized definitions, robust validation rules, and regular data quality audits. Accurate, consistent, and complete data ensures automated systems function as intended and deliver reliable insights.
Even small misconfigurations can generate incorrect risk scores, wasted effort, and compliance gaps. Misapplied rules or thresholds misclassify threats and leave coverage blind spots.
Prevent this by testing rules against known scenarios, reviewing scoring logic routinely, and monitoring configuration changes. Regular validation ensures that risk assessment tools operate correctly and consistently, avoiding surprises in critical decision-making.
Vendors, suppliers, and partners introduce risks that demand their own strategy. Standard risk management approaches often fall short here. Breaches caused by third party vendors increase costs by over $370,000 on average, according to Ponemon. Automation allows organizations to manage these risks efficiently while maintaining full visibility, control, and speed in decision-making. This approach helps companies automate vendor risk management across multiple suppliers and partners.
Manual vendor assessments used to take months of back-and-forth emails, spreadsheets, and follow-ups. Automation reduces this to 2–4 weeks by:
No more hunting for vendor responses or wondering if forms were completed multiple times. Automation ensures assessments are fast, consistent, and accurate.
Point-in-time assessments are like checking your blood pressure once a year. Continuous monitoring gives:
Teams are alerted early, allowing proactive responses instead of reactive firefighting.
Compliance doesn’t have to be a manual slog through frameworks. Automation makes it simple by:
Auditors and management get transparency without manual effort, and your team avoids last-minute scrambles.
A central dashboard acts as a control tower for vendor risk, offering:
No more juggling spreadsheets or piecing together intelligence.
Automation streamlines third-party risk management, reduces manual effort, and ensures continuous oversight. These strategies make managing vendor risks faster, smarter, and far more reliable.
By 2026, AI isn’t just a tool—it’s a game-changer for how organizations automate risk management. Reactive security is history. Predictive, preemptive systems now detect threats before they occur. Digital twins run thousands of “what if” scenarios—from cyberattacks to economic shocks—helping leaders make faster, smarter decisions. Organizations can anticipate problems and respond proactively rather than under pressure.
Edge-based AI catches risks in real time, while cloud partnerships deliver automation as a service. Routine tasks are fully automated, freeing security teams to focus on higher-value work. This boosts efficiency, reduces human error, and ensures critical insights reach decision-makers instantly.
Humans aren’t disappearing. Expert teams guide AI, ensuring decisions remain transparent, fair, and ethical. AI-blockchain integrations instantly verify vendor credentials. Risk management is expanding beyond cybersecurity to include environmental, social, and governance risks.
The future is automated, intelligent, and human-guided. Tech handles the grind. Experts focus on strategy, ethics, and oversight. Organizations embracing this approach won’t just react—they’ll anticipate, prevent, and manage risks with precision and confidence.
Streamline risk, stay ahead of threats, and empower your security team with UprootSecurity — where automation in risk management turns strategy into action.
→ Book a demo today

Senior Security Consultant